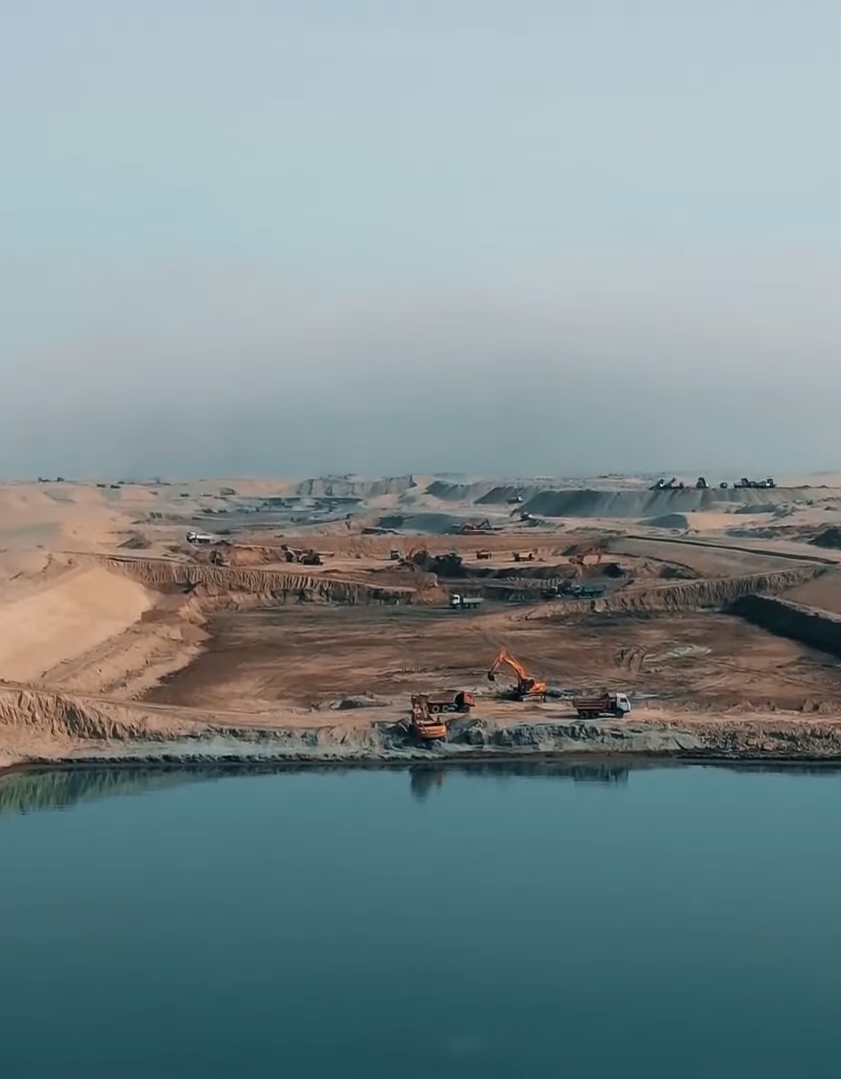
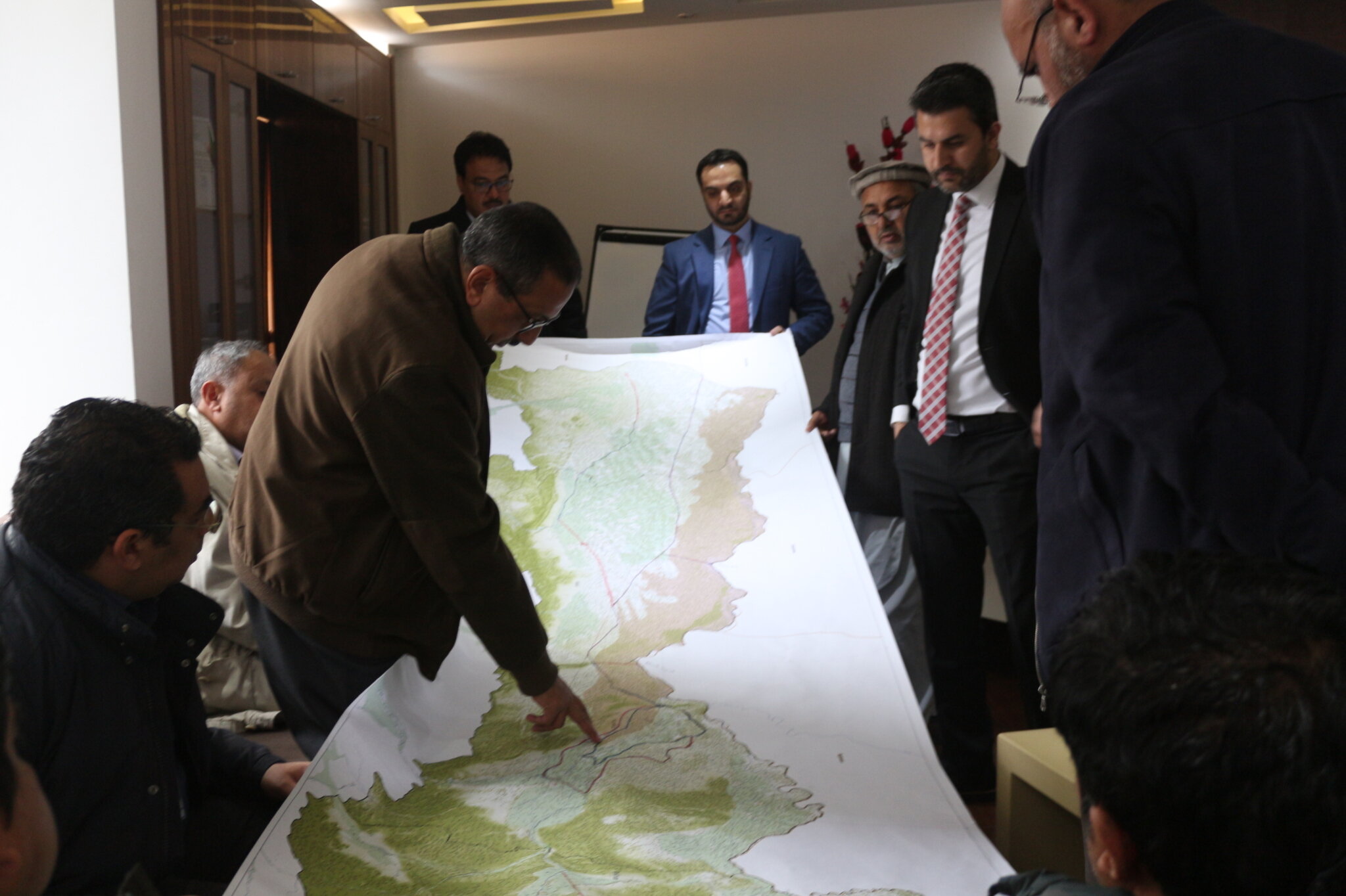
From 2018 to 2021, Adroit implemented USAID’s largest technical feasibility study in Afghanistan, working with several ministries within the then government of Afghanistan to assess the feasibility and viability of a multi-billion dollar irrigation and hydropower project — the Qosh Tepa Irrigation Project — which, if implemented, will provide millions with access to water and power resources, thus transforming Afghanistan’s economy. Adroit focused on a multi-dimensional assessment covering hydrological, engineering, socio-economic, and environmental aspects to recommend the most sustainable intake location.
- 4 Provinces targeted for irrigation development.
- 213,437 km² of surface area of the Amu Darya River Basin assessed.
- 500,000 Hectares of potential irrigable area evaluated.
- $298 Million estimated increase in project benefits with Qosh Tepa intake.
About the Project
As part of its support to agriculture in Afghanistan, from 2018 – 2019, the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) supported the Qosh Tepa Irrigation Scheme and Power Generation (QTISPG) Feasibility Study under USAID’s Strengthening Watershed and Irrigation Management (SWIM) project.
Phase I of the study, completed at the end of 2019, demonstrated the project’s strong potential for development and confirmed its financial and economic feasibility. The study concluded that implementing the proposed project would significantly contribute to the national economy through commercial agriculture and help eradicate poverty by stabilizing and improving livelihoods.
Following the successful completion of Phase I, Adroit implemented Component I of Phase II of the Khush Tepa Irrigation Project Feasibility Study (QTIP FS II) in late 2020. This phase focused on conducting further studies on the proposed intake locations at Qosh Tepa and Kaldar.
Methodology
The primary objectives included conducting detailed hydrological studies and water resource assessments at potential intake locations, specifically at Qosh Tepa and Kaldar in the Amu Darya river basin. These analyses aimed to determine the optimal location for water intake that could support irrigation over 500,000 hectares while ensuring environmental flow requirements and water availability for downstream uses. Adroit Associates focused on a multi-dimensional assessment covering hydrological, engineering, socio-economic, and environmental aspects to recommend the most sustainable intake location.
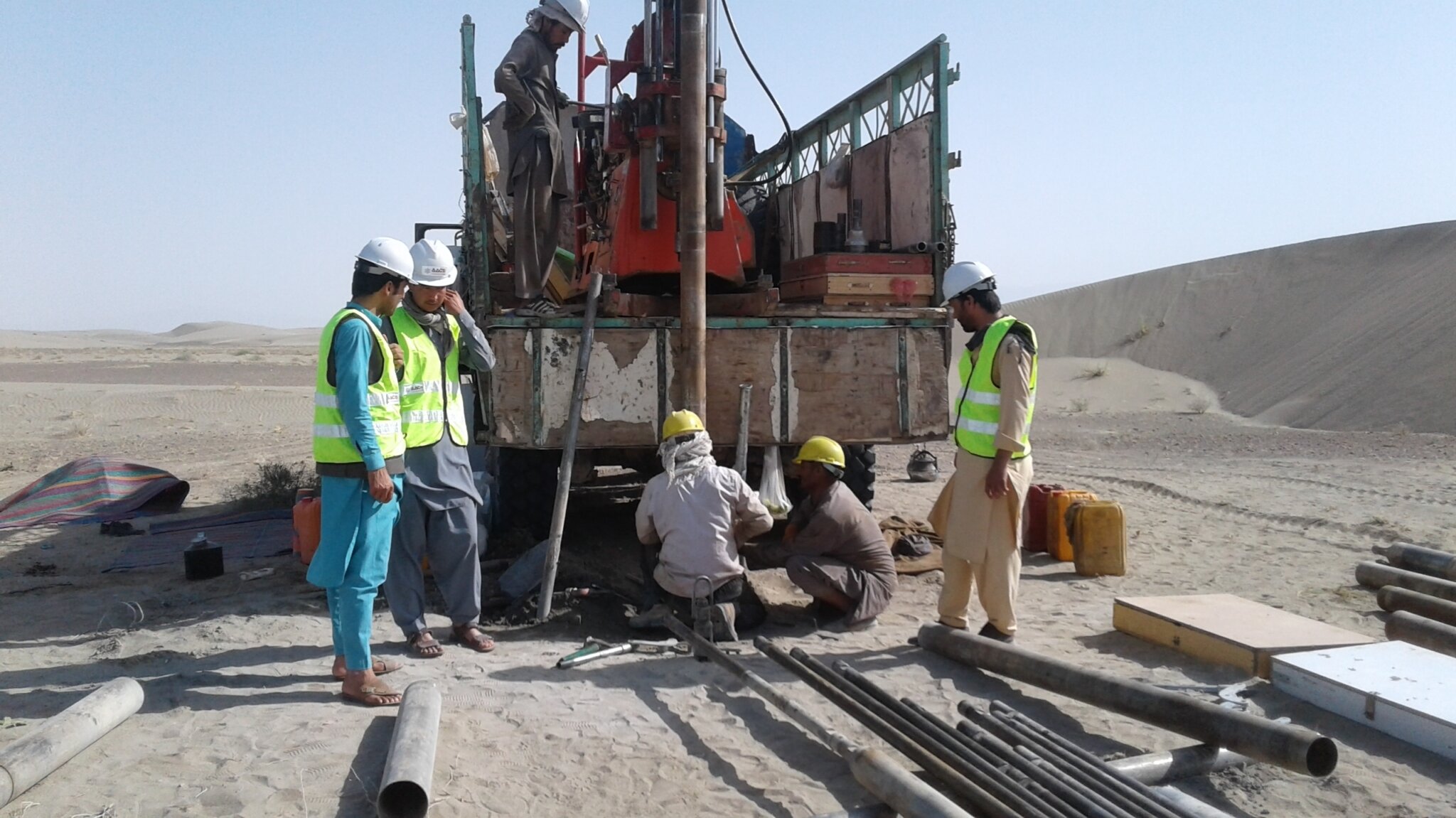
Key tasks undertaken included extensive data collection, development of hydrological and water allocation models — HEC-HMS (Hydrologic Modeling System) and WEAP (Water Evaluation and Planning) and updating environmental and social assessments from previous phases. This rigorous approach ensured that all potential impacts were considered and addressed, positioning the study for success while fostering sustainability and community involvement.
Project Implementation
The implementation phase was designed to actualize the agricultural enhancement and economic development potentials identified during the feasibility studies, setting the groundwork for enduring impacts.
In this critical stage, the project’s scope included constructing water intake structures, laying out expansive irrigation networks, and establishing power generation facilities. Each component is carefully integrated with environmental and social considerations to mitigate any potential negative impacts.
- Environmental Compliance and Assessment To align with USAID’s Environmental Regulations and the regulations of Afghanistan’s National Environmental Protection Agency (NEPA), Adroit developed a comprehensive Scoping Statement (SS) and Environmental Assessment (EA). This preliminary assessment was crucial in identifying significant potential environmental and social impacts of the QTISPG, and it formed the basis for a detailed Environmental and Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) planned for the next phase.
- Community and Stakeholder Engagement The implementation phase was marked by robust engagement with local communities and stakeholders. This involved direct consultations and rapid field surveys in the Qosh Tepa region, which were conducted to gather firsthand information and to integrate community insights into project planning. Key stakeholders included local government bodies like the Directorate of Agriculture, Irrigation, and Livestock (DAIL), the Director of NEPA, and the National Water Affairs Regulatory Authority (NWARA), along with community leaders and residents.
- Socio-environmental Integration Adroit Associates prioritized the integration of socio-environmental considerations into all phases of project implementation. Initial data collection facilitated by rapid surveys and public consultations informed the preparation of a detailed Resettlement Action Plan (RAP) and ensured gender participation. This groundwork was vital for crafting an informed and comprehensive Environmental and Social Management Plan (ESMP) for subsequent phases, which will include monitoring and mitigation strategies to minimize environmental and social impacts during construction and operation.